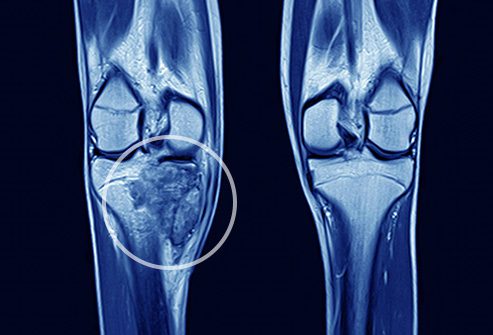
Bone cancer is a rare type of cancer that begins in the cells that make up the bones. It can affect any bone in the body, but most commonly occurs in the long bones of the arms and legs. Understanding bone cancer, its symptoms, treatments, and prognosis is crucial for adults who have been diagnosed with this condition.
Symptoms of Bone Cancer
The symptoms of bone cancer can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor. Some common symptoms of bone cancer include:
1. Pain: Persistent and worsening bone pain is the most common symptom of bone cancer. The pain may be worse at night and may not be relieved by rest or over-the-counter pain medications.
2. Swelling: Swelling and tenderness over the affected area may be present. In some cases, a noticeable lump or mass may be felt.
3. Fractures: Bone cancer can weaken the affected bone, leading to an increased risk of fractures.
4. Fatigue: Unexplained fatigue and weakness may be present, especially if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
5. Weight loss: Unintended weight loss can occur as a result of the cancer affecting the body’s metabolism.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by conditions other than bone cancer. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to see a doctor for further evaluation and diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Bone Cancer
In order to diagnose bone cancer, a doctor may perform a variety of tests, including:
1. Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans can help identify the location, size, and extent of the tumor.
2. Biopsy: A biopsy is the definitive way to diagnose bone cancer. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is removed from the affected bone and examined under a microscope for the presence of cancer cells.
3. Blood tests: Blood tests may be performed to look for markers that indicate the presence of bone cancer.
Once a diagnosis of bone cancer has been confirmed, further tests may be done to determine the stage of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment of Bone Cancer
The treatment of bone cancer depends on the type, location, and stage of the cancer, as well as the overall health and preferences of the patient. The main treatment options for bone cancer may include:
1. Surgery: Surgery is often the primary treatment for bone cancer. The goal of surgery is to remove the cancerous tumor and any surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that all cancer cells are eradicated.
2. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be used before or after surgery to shrink the tumor, kill any remaining cancer cells, or reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
3. Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It may be used as a primary treatment or in combination with surgery and chemotherapy.
4. Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target the unique characteristics of cancer cells, often with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
Prognosis for Adults with Bone Cancer
The prognosis for bone cancer can vary widely depending on the type of bone cancer, the stage at which it is diagnosed, and the overall health of the patient. In general, the prognosis for adults with bone cancer has improved in recent years due to advances in treatment and early detection.
For localized bone cancer, the five-year survival rate is around 70-85%. However, for bone cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is lower, at around 15-30%.
It is important to note that these statistics are general and may not apply to every individual. Factors such as the type of bone cancer, the grade and stage of the cancer, and the patient’s response to treatment can all impact the prognosis.
In some cases, bone cancer may recur after treatment. Close monitoring by a healthcare provider is important to detect any signs of recurrence and to provide appropriate care if needed.
In conclusion, understanding bone cancer, its symptoms, treatments, and prognosis is essential for adults who have been diagnosed with this condition. If you experience any symptoms of bone cancer, it is important to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and diagnosis. With early detection and advances in treatment, the prognosis for adults with bone cancer has improved, offering hope for better outcomes and quality of life.












