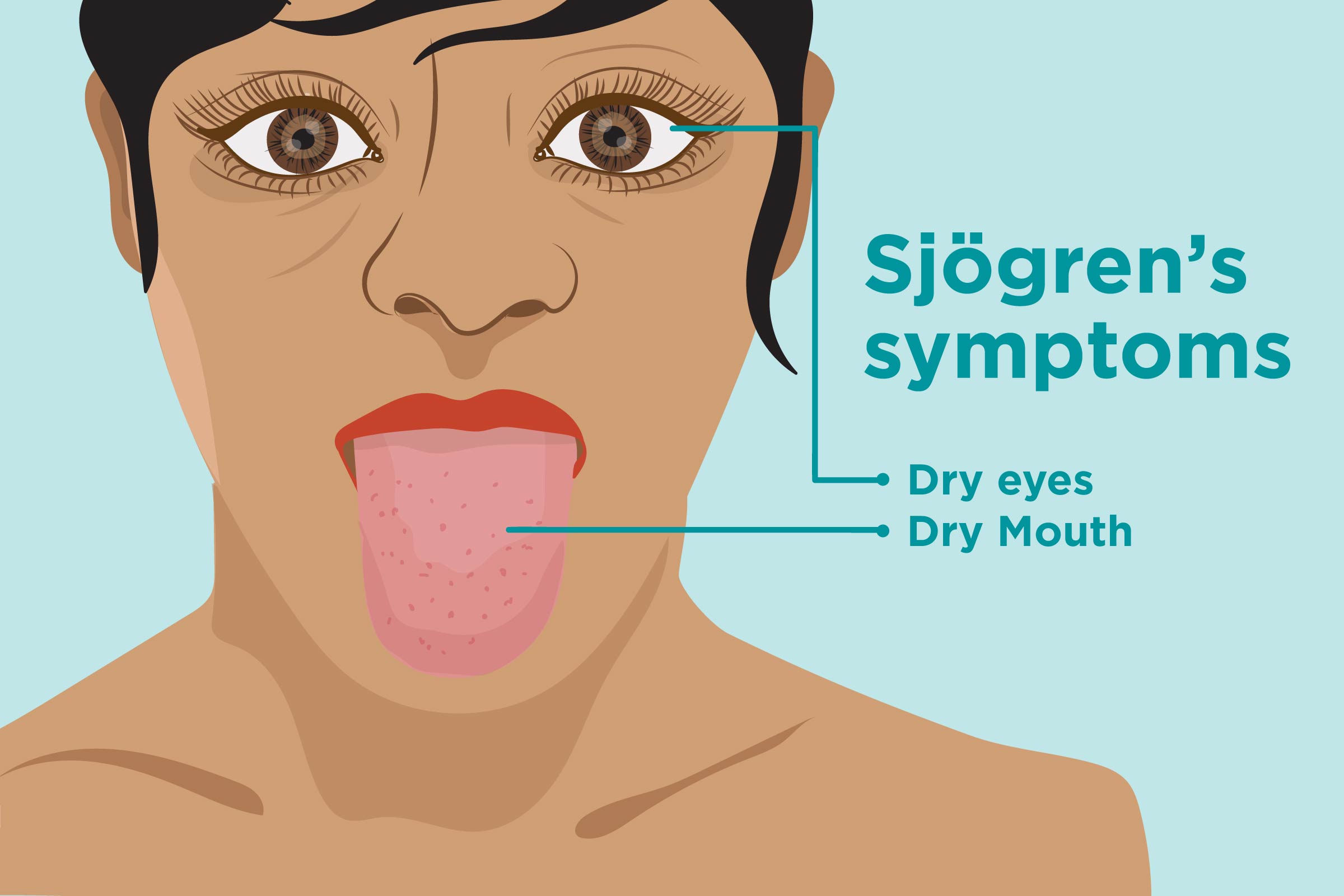

 Sjögrenʼs syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the moisture-producing glands in the body, leading to symptoms such as dry eyes and dry mouth. This condition can also affect other parts of the body, causing a wide range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms of Sjögrenʼs syndrome is important for early detection and management of the condition.
Sjögrenʼs syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the moisture-producing glands in the body, leading to symptoms such as dry eyes and dry mouth. This condition can also affect other parts of the body, causing a wide range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms of Sjögrenʼs syndrome is important for early detection and management of the condition.
In this article, we will discuss the various symptoms of Sjögrenʼs syndrome and how they can manifest in different parts of the body. By recognizing these symptoms, individuals can seek appropriate medical intervention and support to manage the effects of this condition.
Dry eyes
One of the most common symptoms of Sjögrenʼs syndrome is dry eyes, which can cause discomfort, irritation, and a gritty sensation. The lack of sufficient moisture in the eyes can lead to blurred vision, light sensitivity, and difficulty wearing contact lenses. Individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome may experience persistent dryness in their eyes, leading to chronic eye problems that require regular lubrication and management.
It is important for individuals experiencing dry eyes to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause of their symptoms, especially if they suspect they may have Sjögrenʼs syndrome. Ophthalmologists and rheumatologists can work together to provide comprehensive care for managing dry eyes and other symptoms associated with Sjögrenʼs syndrome.
Dry mouth
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is another common symptom of Sjögrenʼs syndrome that can significantly impact a person’s oral health and overall well-being. The lack of saliva in the mouth can lead to difficulties in speaking, swallowing, and tasting food. Individuals with dry mouth may also experience frequent mouth sores, bad breath, and an increased risk of dental decay and gum disease.
Managing dry mouth in Sjögrenʼs syndrome often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including dental care, oral hydration, and lifestyle modifications. Dentists can provide strategies for maintaining oral health, while healthcare providers can offer treatments to stimulate saliva production and alleviate the symptoms of dry mouth.
Fatigue
Many individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome experience persistent fatigue that can significantly impact their daily functioning and quality of life. This chronic fatigue can be debilitating and may not improve with rest, leading to challenges in maintaining work, social, and personal activities. Understanding the underlying causes of fatigue in Sjögrenʼs syndrome is important for developing effective management strategies and support for individuals with this condition.
Healthcare professionals can work with individuals to address the factors contributing to their fatigue, such as pain, sleep disturbances, and psychological well-being. By identifying and managing these factors, individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome can better cope with their symptoms and improve their overall energy levels and well-being.
Joint pain
Sjögrenʼs syndrome can also cause joint pain and stiffness, which can mimic the symptoms of other rheumatic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome may experience pain, swelling, and limited mobility in their joints, particularly in the hands, wrists, and knees. Understanding the nature of joint pain in Sjögrenʼs syndrome is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of this symptom.
Rheumatologists can conduct thorough assessments to evaluate the extent of joint involvement in Sjögrenʼs syndrome and develop personalized treatment plans to address these symptoms. Physical therapy, pain management, and medications may be recommended to alleviate joint pain and improve joint function in individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome.
Skin problems
Individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome may experience various skin problems, including dry skin, rashes, and itchiness. The lack of moisture in the skin can lead to irritation, sensitivity, and an increased risk of skin infections. Dermatologists can assess these skin problems and provide appropriate skin care recommendations to manage the symptoms of Sjögrenʼs syndrome.
Using gentle skincare products, moisturizers, and protecting the skin from environmental factors can help individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome maintain healthy skin and alleviate the discomfort associated with skin problems. Healthcare providers can also address underlying systemic factors contributing to skin problems, such as inflammation and immune dysfunction, to improve skin health in individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome.
Gastrointestinal symptoms
Aside from dry mouth, individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome may also experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, heartburn, and abdominal pain. The lack of saliva and moisture in the digestive tract can lead to challenges in food consumption and digestion. Recognizing and addressing these gastrointestinal symptoms is important for maintaining proper nutrition and gastrointestinal health in individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome.
Gastroenterologists and nutritionists can work together to develop dietary and lifestyle strategies to address the gastrointestinal symptoms of Sjögrenʼs syndrome. Managing these symptoms can improve a person’s ability to consume and digest food, reducing the impact of gastrointestinal problems on their overall health and well-being.
Pulmonary complications
Sjögrenʼs syndrome can affect the lungs, leading to pulmonary complications such as chronic cough, shortness of breath, and recurrent respiratory infections. Individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome may experience difficulties in breathing and respiratory function, which can significantly impact their overall health and quality of life. Identifying and managing pulmonary complications in Sjögrenʼs syndrome is essential for providing comprehensive care for affected individuals.
Pulmonologists can assess respiratory function and provide appropriate interventions to address the pulmonary complications of Sjögrenʼs syndrome. This may include respiratory therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications to improve breathing and reduce the frequency and severity of respiratory symptoms in individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome.
Neurological symptoms
Some individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome may experience neurological symptoms, including cognitive impairment, headaches, and nerve pain. These symptoms can impact a person’s cognitive function, mood, and overall neurological well-being. It is important to recognize and address neurological symptoms in Sjögrenʼs syndrome to provide appropriate support and management for affected individuals.
Neurologists can assess neurological function and provide interventions to address cognitive impairment, headaches, and nerve pain in individuals with Sjögrenʼs syndrome. Cognitive rehabilitation, pain management, and neurological medications may be recommended to alleviate these symptoms and improve neurological well-being in affected individuals.
Systemic complications
Sjögrenʼs syndrome can also lead to systemic complications affecting various organs and body systems, such as the kidneys, liver, and blood vessels. Understanding the systemic effects of Sjögrenʼs syndrome is important for comprehensive management and support for individuals with this condition.
Healthcare professionals specializing in the affected organ systems can assess the systemic complications of Sjögrenʼs syndrome and provide appropriate interventions to address these effects. This may include medication management, lifestyle modifications, and monitoring of organ function to minimize the impact of systemic complications on a person’s overall health and well-being.












