Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that causes tumors to form on nerve tissue. These tumors can develop anywhere in the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. There are three types of neurofibromatosis: NF1, NF2, and Schwannomatosis. Each type has its own set of symptoms, but they all share the characteristic of tumors forming on nerve tissue. In this article, we will explore the symptoms of neurofibromatosis and how they can impact those affected by the condition.
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary widely among individuals with neurofibromatosis. Some people may have mild symptoms that are barely noticeable, while others may have more severe symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life. Additionally, many symptoms of neurofibromatosis are not present at birth and may develop over time. Early detection and treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve overall health outcomes for those with neurofibromatosis.
1. Café-au-lait spots
One of the most common early signs of neurofibromatosis is the presence of café-au-lait spots, which are flat, brown patches on the skin. These spots can vary in size and number, and they are typically present from birth. While café-au-lait spots are common in many children, individuals with neurofibromatosis tend to have larger and greater numbers of these spots. The presence of multiple café-au-lait spots can be a key indicator of neurofibromatosis and should prompt further evaluation by a healthcare professional.
In addition to café-au-lait spots, individuals with neurofibromatosis may also develop freckles in the armpits and groin, known as axillary or inguinal freckling. These skin changes are often one of the earliest signs of the condition and can help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis.
2. Optic gliomas
Optic gliomas are tumors that develop along the optic nerve, which connects the eye to the brain. These tumors can cause a variety of visual symptoms, including blurry vision, double vision, and loss of peripheral vision. In some cases, optic gliomas may also lead to the development of a bulging, misshapen eye. It’s important for individuals with neurofibromatosis to have regular eye exams to monitor for the presence of optic gliomas and to address any changes in vision that may occur.
Early detection and treatment of optic gliomas are crucial to preserving vision and preventing further complications. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the size and location of the tumor. Close collaboration between ophthalmologists and neurologists is essential to ensure the best possible outcomes for individuals with neurofibromatosis and optic gliomas.
3. Neurological complications
Neurofibromatosis can lead to a range of neurological complications, including headaches, seizures, and learning disabilities. Tumors that develop in the brain or spinal cord can cause pressure on surrounding tissues, leading to symptoms such as persistent headaches and seizures. In some cases, individuals with neurofibromatosis may also experience cognitive or behavioral challenges, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism spectrum disorders.
It’s important for individuals with neurofibromatosis to undergo regular neurological assessments to monitor for any changes in cognitive function and to address any symptoms that may arise. Treatment options may include medication to manage seizures or cognitive and behavioral therapies to support individuals with learning disabilities.
4. Bone abnormalities
Individuals with neurofibromatosis may develop bone abnormalities, including scoliosis (curvature of the spine) and thinning of the long bones in the arms and legs. These bone changes can cause physical discomfort and may impact mobility and overall quality of life. Regular monitoring by an orthopedic specialist is essential to identify and address any bone abnormalities that may develop in individuals with neurofibromatosis.
Treatment options for bone abnormalities may include bracing to support the spine, physical therapy to improve strength and flexibility, and surgical interventions to correct severe spinal curvature. Early intervention is key to preventing further progression of bone abnormalities and ensuring optimal musculoskeletal health for individuals with neurofibromatosis.
5. Hearing loss
Neurofibromatosis can also lead to hearing loss, especially in individuals with NF2. Tumors that develop on the nerves responsible for hearing (vestibulocochlear nerves) can cause gradual hearing loss, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and balance issues. Regular hearing evaluations and auditory screenings are essential for individuals with neurofibromatosis to monitor for any changes in hearing function and to address any symptoms that may arise.
Treatment options for hearing loss associated with neurofibromatosis may include hearing aids, cochlear implants, or surgical interventions to remove tumors and preserve hearing function. Close collaboration between otolaryngologists and audiologists is essential to provide comprehensive care for individuals with neurofibromatosis who are experiencing hearing loss.
6. Cardiovascular complications
Neurofibromatosis can also impact the cardiovascular system, leading to complications such as high blood pressure and narrowing or weakening of blood vessels. Individuals with neurofibromatosis should undergo regular cardiovascular assessments, including blood pressure monitoring and imaging studies to evaluate the health of the blood vessels and heart. Early detection and management of cardiovascular complications are essential to prevent further progression of the condition and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Treatment options for cardiovascular complications associated with neurofibromatosis may include medication to manage high blood pressure, lifestyle modifications to improve cardiovascular health, and surgical interventions to address any structural abnormalities in the blood vessels. Close collaboration between cardiologists and vascular specialists is essential to provide comprehensive care for individuals with neurofibromatosis who are at risk for cardiovascular complications.
7. Gastrointestinal issues
Neurofibromatosis can also affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to complications such as abdominal pain, constipation, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Tumors that develop in the gastrointestinal tract can cause a variety of symptoms, and individuals with neurofibromatosis should undergo regular evaluations by a gastroenterologist to monitor for any changes in gastrointestinal function. Treatment options may include medication to manage symptoms, dietary modifications to improve digestive health, and surgical interventions to address any gastrointestinal tumors that may develop.
Close collaboration between gastroenterologists and nutritionists is essential to provide comprehensive care for individuals with neurofibromatosis who are experiencing gastrointestinal issues. Regular monitoring and early intervention can help individuals with neurofibromatosis maintain optimal gastrointestinal health and overall well-being.
8. Endocrine disturbances
Neurofibromatosis can lead to disturbances in the endocrine system, including hormonal imbalances and complications such as early puberty or delayed growth. Regular assessments by an endocrinologist are essential to monitor for any changes in hormonal function and to address any symptoms that may arise. Treatment options may include hormone therapy to manage imbalances and promote healthy growth and development.
Close collaboration between endocrinologists and pediatricians is essential to provide comprehensive care for children with neurofibromatosis who may be experiencing endocrine disturbances. Early detection and management of endocrine complications are crucial to promoting healthy growth and development in individuals with neurofibromatosis.
9. Psychological and social challenges
Living with neurofibromatosis can present a range of psychological and social challenges, including anxiety, depression, and social stigma. Individuals with neurofibromatosis should have access to mental health support and resources to address any emotional or psychological symptoms that may arise. Additionally, individuals with neurofibromatosis may benefit from support groups and community resources to connect with others who understand their experiences and provide a supportive network.
Close collaboration between mental health professionals and social workers is essential to provide comprehensive support for individuals with neurofibromatosis who may be experiencing psychological or social challenges. It’s important for individuals with neurofibromatosis to have access to a multidisciplinary care team that can address their medical, emotional, and social needs.
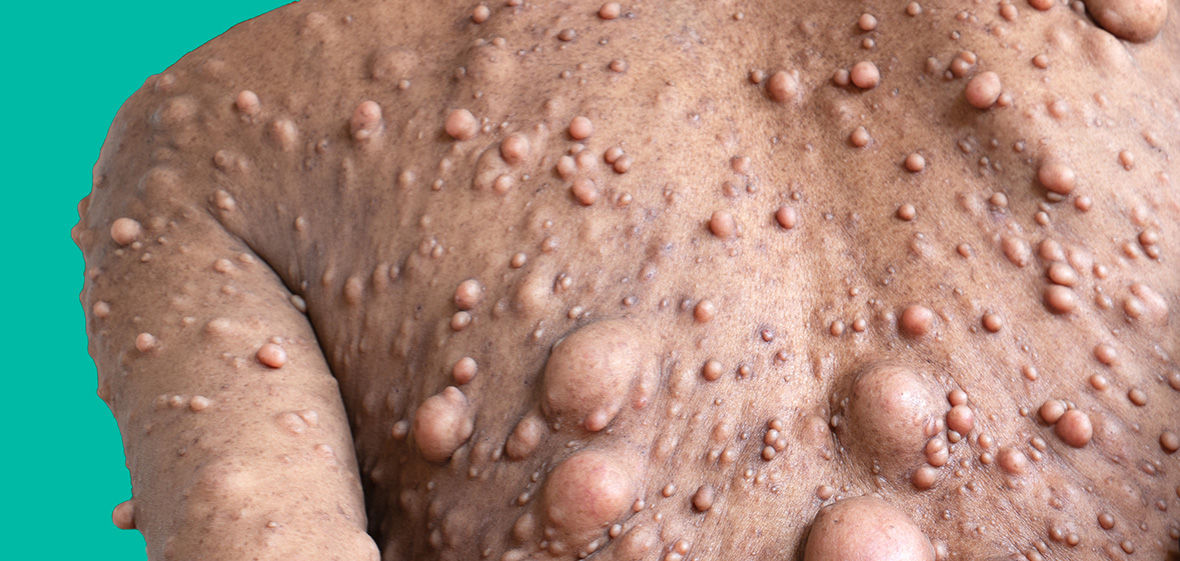
10. Skin changes and tumors
One of the hallmark features of neurofibromatosis is the development of neurofibromas, which are benign tumors that develop on or under the skin. These tumors can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, itching, and cosmetic concerns. Individuals with neurofibromatosis should undergo regular skin examinations by a dermatologist to monitor for the development of neurofibromas and to address any symptoms that may arise.
Treatment options for skin changes and tumors associated with neurofibromatosis may include medication to manage symptoms, laser therapy to improve skin appearance, and surgical interventions to remove tumors that are causing discomfort or functional impairment. Close collaboration between dermatologists and plastic surgeons is essential to provide comprehensive care for individuals with neurofibromatosis who are experiencing skin changes and tumors.












